Major Effects of Low Doses of ZKCPr1 on Excess Visceral and Metabolic Disorders
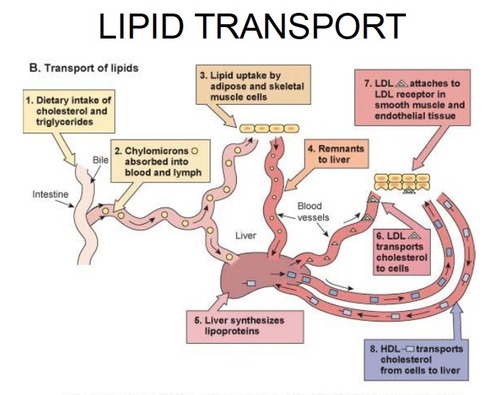
ZKCPr1 inhibits fat transport via blocking binding of fats to chylomicrons, the fat
transporting proteins. [The scheme below shows the basic elements of the fat transport.]
On the other hand, since the visceral fat metabolizes fat in the form of sweat and pee
quicker than subcutaneous fat (mostly responsible for general obesity), this explains
why low doses of ZKCPr1 preferentially inhibit accumulation of fat in the visceral tissue.
Then, higher doses of ZKCPr1 also inhibit accumulation of fat in the subcutaneous fat
tissue largely contributing to general obesity.
 Other Properties of ZKCPr1
Other Properties of ZKCPr1
- It does not cause side effects
- It is resistant to heat (up to 65 Celsius) and proteases: As a result it has an
up to 10 days of half-life time in the human circulation (~4 days in mice)
- It inactivates Lysopolysaccharide and extracellular ATP, important inflammatory mediators
- It is an antitumor and anticachectic agent also protecting the bone marrow
against the toxic effects of cancer drugs
Availibility: It is available from commercial sources.
 Home
Major Results
Mechanism
Applications
Advisors
Management
Contact Us
Home
Major Results
Mechanism
Applications
Advisors
Management
Contact Us
